
doi:10.A subreddit designed for discussion of supplements and nutraceuticals for health, performance, or any intended (or not intended) purpose. Multifarious beneficial effect of nonessential amino acid, glycine:a review. Razak MA, Begum PS, Viswanath B, Rajagopal S. Pre-sleep casein protein ingestion: new paradigm in post-exercise recovery nutrition. Whey protein supplementation enhances whole body protein metabolism and performance recovery after resistance exercise: a double-blind crossover study. Pectin and pectin-based composite materials: beyond food texture. Lara-Espinoza C, Carvajal-Millán E, Balandrán-Quintana R, et al. A review of the effects of collagen treatment in clinical studies. Dietary supplements: what you need to know.

National Institutes of Health's Office of Dietary Supplements. A review of gelatin source authentication methods. Gelatin hydrogels with eicosapentaenoic acid can prevent osteoarthritis progression in vivo in a mouse model. The anti-inflammatory effect of bovine bone-gelatin-derived peptides in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages cells and dextran sulfate sodium-snduced C57BL/6 mice.
#COLLAGEN VS GELATIN THM SKIN#
Protective effects of tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus) skin gelatin hydrolysates on osteoporosis rats induced by retinoic acid. Effects of dietary gelatin hydrolysates on bone mineral density in magnesium-deficient rats. Protective effect of gelatin peptides from Pacific cod skin against photoaging by inhibiting the expression of MMPs via MAPK signaling pathway. The anti-skin-aging effect of oral administration of gelatin from the swim bladder of Amur sturgeon ( Acipenser schrenckii). Liu D, Nikoo M, Boran G, Zhou P, Regenstein JM. Bovidae-based gelatin: extractions method, physicochemical and functional properties, applications, and future trends. Samatra MY, Noor NQIM, Razali UHM, et al. Natural-based biomaterial for skin wound healing (gelatin vs. Glycine is a part of many important processes in the human body, such as protein synthesis and nerve signal transmission.

As a supplement, pectin may act as a prebiotic, help lower blood sugar, and decrease cholesterol levels. Pectin is a source of fiber that comes from apples and other fruits and vegetables. Pectin: Like gelatin, pectin is often used to thicken and stabilize certain foods.Evidence suggests that collagen may be beneficial for aging skin, bone health, sarcopenia (muscle wasting), wound healing, osteoarthritis, and other health concerns.
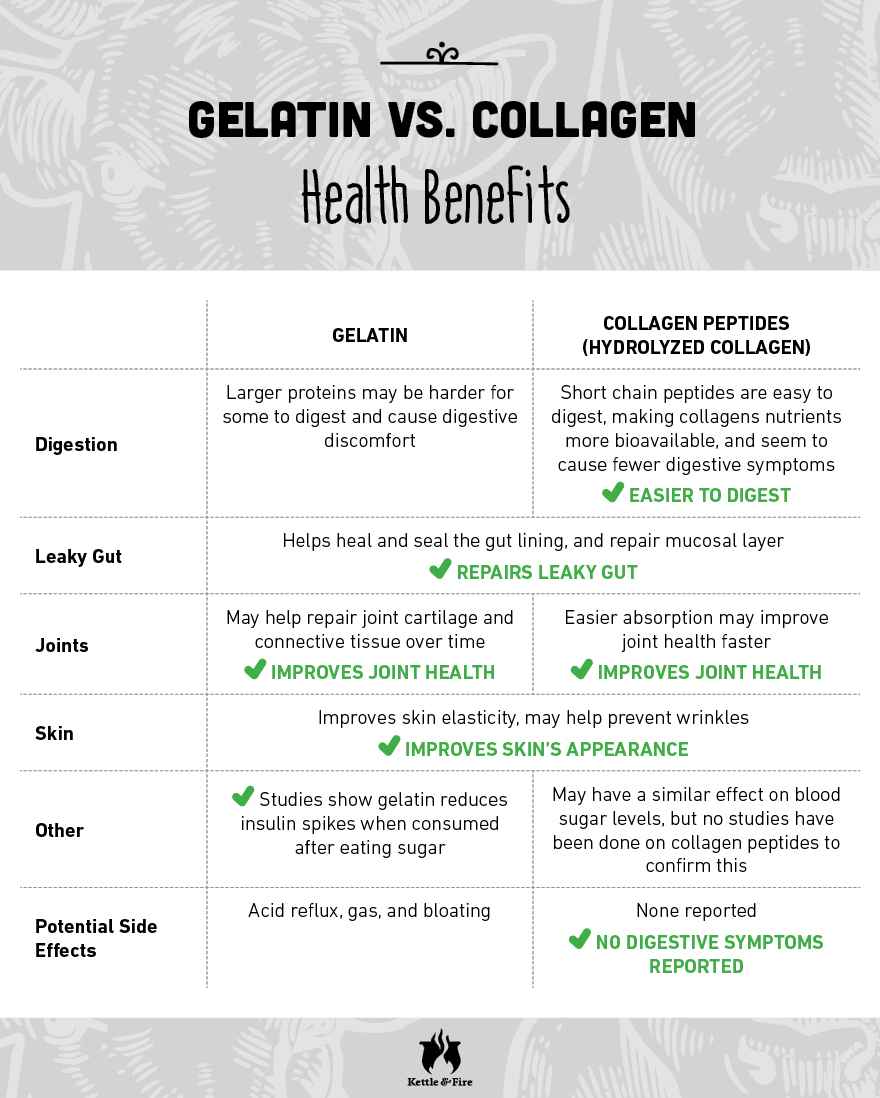
Collagen: Since gelatin is derived from collagen, it makes sense that collagen supplements work similarly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
